WAFFLE Cushion Range – Prevent and Treat Stages I-IV Pressure Ulcers
 From one surface to another, wound care and prevention is an ongoing process for many caregivers. Our Waffle Cushion range helps provide comfort and prevention in the areas where many people spend the majority of their day.
From one surface to another, wound care and prevention is an ongoing process for many caregivers. Our Waffle Cushion range helps provide comfort and prevention in the areas where many people spend the majority of their day.
The conditions of seating applications are often overlooked in hospitals, nursing homes and in homecare due to the focus on bedding.
But when you consider the amount of time that people spend sitting upright, whether in wheelchairs, daychairs, or other hard surfaces, it’s vital to consider covering these surfaces to aid in seating comfort and prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers up through Stage IV.
All EHOB WAFFLE®️ Cushions a feature a low profile design that immerses the client into the cushion, cradling around natural bony areas to lift the patient off the seating surface.
Our seating cushions help provide comfort whilst providing a clinically efficient prevention tool.
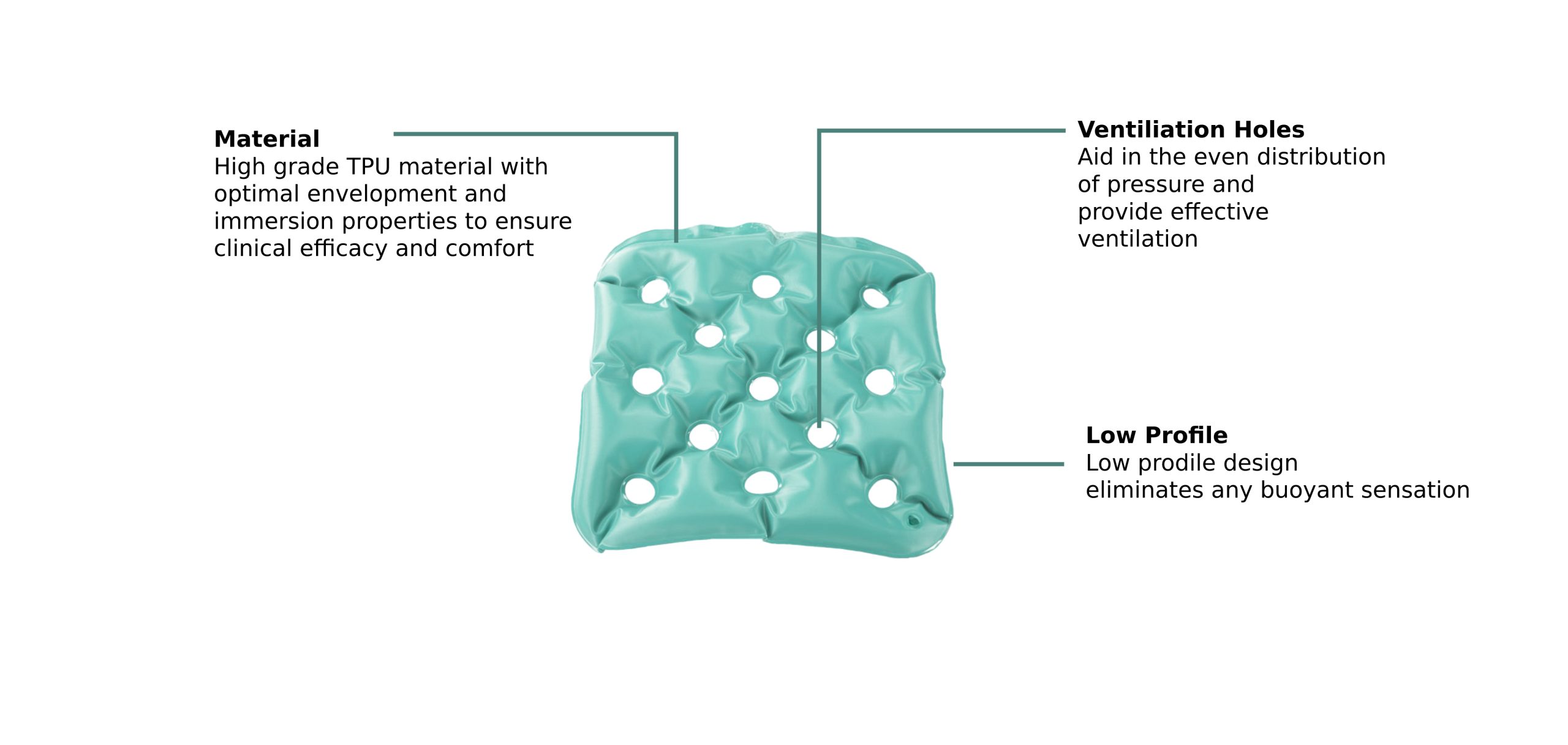
The WAFFLE Cushion range helps reduce your risk of pressure injuries and helps improve comfort when sitting.
- Lifts sit bones and tailbone off the surface when properly inflated
- Allows your body to sink into the product, helping increase comfort
- Unique venting holes provide airflow to keep you comfortable
Pressure injuries (bed sores) can develop when pressure is put on bony areas for long periods of time. This can occur when people with fragile skin are moved to their chair.
- 2.5 million patients develop pressure injuries each year1
- 2 hours is the potential length of time pressure injuries can develop2

Purchase this product
Download the product brochure: WAFFLE® & TruVue® Range
Visit our Inflation Guide page